You can click here to the Forex Margin & Leverage Calculator page, or read this guide article.
Imagine this scenario: you've spotted an excellent trading opportunity, and the EUR/USD pair looks set to rise. You have $1,000 in your account and are confidently ready to make a big move. You choose 100:1 leverage and place a 1-lot order. The moment you click “Buy,” your platform pops up a terrifying warning—"Insufficient margin," or worse, the trade is outright rejected.
How could this happen? What went wrong? The real reason is that you overestimated the benefits of leverage while underestimating its pitfalls. Without a thorough understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of leverage, you cannot assess your account's risk tolerance. In the foreign exchange trading field, leverage is indeed a powerful tool. However, for most people without a trading system and trading discipline, leverage could be the TNT that destroys your account. Therefore, you may need to thoroughly understand leverage, carefully calculate it, control it, and use it reasonably. This is also the inevitable path for every trader to transition from a novice to a more mature trader.
And it all starts with a simple calculation.
Alright, you can get the answer immediately. But if you want to truly take control of your trading destiny rather than just getting a number, keep reading. This article will be your most comprehensive and practical guide to understanding forex margin and leverage.
Ⅰ. What are Forex Margin and Leverage? (Basic Concepts)
1. Let’s understand these two terms in the simplest way possible.
Margin: This is a deposit. You want to trade a contract worth $100,000, but you only have $5,000 in your account. The broker says, “No problem, I trust you, but you need to deposit a portion of the funds with me first, just in case you incur losses and walk away.” The money you deposit is the margin. It is the portion of your account funds that is "locked" or "tied up."
Leverage: This refers to the borrowing ratio. Continuing with the previous example, the broker is willing to lend you $95,000, plus your own $5,000, to trade a $100,000 contract. The leverage you are using is Total Trade Value / Your Funds = 100,000 / 5,000 = 20, which is a 20:1 leverage ratio.
2. The relationship between them is: Leverage determines how much margin you need to deposit.
The higher the leverage, the less margin you need to deposit, and vice versa.
The following flowchart clearly illustrates this process:
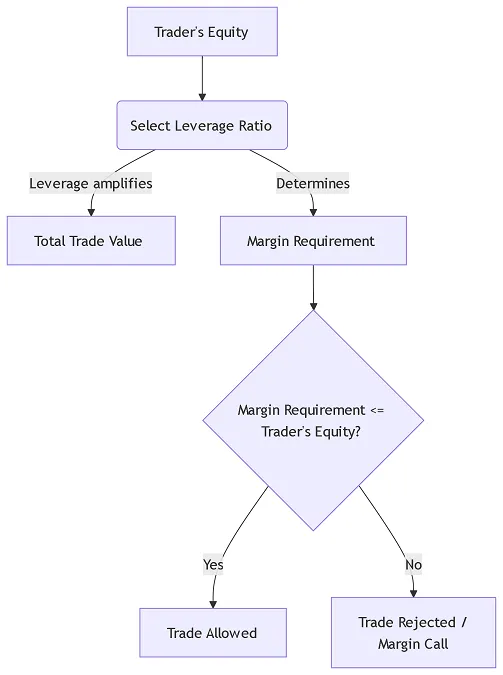
So, when you search for "foreign exchange margin and leverage calculator," your core intention is: "Given my current account funds and chosen leverage, how much margin deposit does the broker require for this trade?" Our calculator was designed to answer this question instantly.
Ⅱ. How to use our forex margin calculator?
Our tool is designed to be extremely simple; you only need a few steps to obtain precise results. Here is a detailed usage guide:
1. Select the trading instrument (Currency Pair): Choose the currency pair you wish to trade from the dropdown menu, such as Euro/US Dollar (EUR/USD).
2. Select Account Currency: What currency is your trading account funded in?USD, EUR, or GBP? This is important because it involves currency conversion.
3. Enter Lot Size: A standard lot is 1.0, a mini lot is 0.1, and a micro lot is 0.01.
4. Select Leverage Ratio: Choose the leverage offered by your broker from the list, such as 50:1, 100:1, 200:1, 500:1, etc.
5. Click "Calculate": The required margin amount will be displayed immediately.
Give it a try! You can adjust the values freely, such as changing the leverage from 100:1 to 400:1, and see how the margin requirement drops sharply—this visually demonstrates the “temptation” of high leverage.
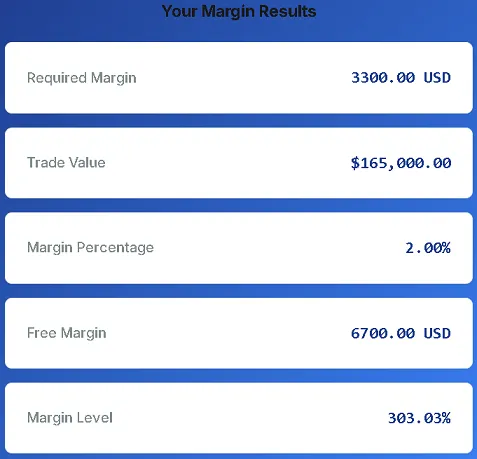
Ⅲ. Forex Margin Calculation Formula (Fully Transparent)
1. We believe you should understand the principles behind the tools you use. This is not a "black box." The foreign exchange margin calculation formula is:
Required Margin = (Lot Size × Contract Size × Opening Price) / Leverage Ratio
Lot Size: As mentioned above, 1.0, 0.1, etc.
Contract Size: The contract size for 1 standard lot is typically 100,000 units of the base currency (for EUR/USD, this is 100,000 euros).
Open Price: The price at which you plan to enter the trade.
Leverage Ratio: The leverage you choose, such as 100.
2. Example:
Assume you want to buy 1 standard lot (1.0 lot) of EUR/USD at the price of 1.0850.
Your account currency is USD, and you have chosen a leverage ratio of 100:1.
Applying the formula:
Required margin = (1.0 × 100,000 × 1.0850) / 100 = (108,500) / 100 = 1,085 USD
This means that to open this position, your account must have at least 1,085 USD available as margin, which will be locked. Our calculator performs this calculation. Understanding the formula allows you to verify the accuracy of the results at any time, enabling you to trade with greater confidence.
IV. Why is leverage a double-edged sword?
1. This is the core part of this article. High leverage allows you to leverage larger trades with less money, but it amplifies not only profits but also losses.
Let's look at a contrasting table that shows the starkly different effects of a trade on your account equity under different leverage ratios:
| Scenario | Account Balance | Leverage Ratio | Trade Size | Required Margin | Price Fluctuation | Profit/Loss Amount | Account Balance Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Leverage | 10,000 USD | 10:1 | 1 standard lot (≈ 100,000 USD) | 10,000 USD | -100 pips | -1,000 USD | 9,000 USD (-10 %) |
| High Leverage | 10,000 USD | 100:1 | 1 standard lot (≈ 100,000 USD) | 1,000 USD | -100 pips | -1,000 USD | 9,000 USD (-10 %) |
| Ultra-High Leverage (Disaster) | 1,000 USD | 500:1 | 1 standard lot (≈ 100,000 USD) | 200 USD | -20 pips | -200 USD | 800 USD (-20 %) |
Note: Calculations are approximate and assume trading EUR/USD.
2. Did you notice?
The first two rows show that the same volatility and the same profit/loss amounts have the same impact on the account balance. High leverage does not reduce the loss per pip.
The most critical part is the third row! A trader with only 1,000 USD in their account using 500:1 leverage to trade 1 standard lot would suffer a 20% loss from just a 20-pip adverse movement (which can happen instantly in the forex market). A typical 50-point fluctuation is sufficient to cause this account to margin call.
This is the terrifying aspect of leverage. It drastically reduces your margin of error. A minor, normal reversal in the market, amplified by extremely high leverage, can turn into a disaster.
3. According to data from authoritative institutions, the vast majority of retail forex traders are losing money.
The UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) noted in its report that over 76% of retail forex clients are in a loss-making state. Data from the US National Futures Association (NFA) also consistently shows a similarly high loss ratio. Excessive use of high leverage is the primary cause of this phenomenon.
Therefore, the correct trading process is not "open a position first, then assess the situation." Instead, it is:
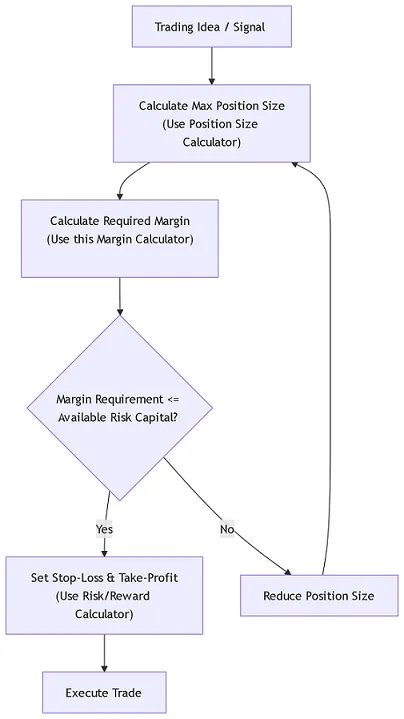
Ⅴ. Common mistakes when using leverage and how to avoid them
1. Mistake One: Blindly using the highest leverage available.
Scenario: If a broker offers 500:1 leverage, using it to the fullest without hesitation.
Solution: Choose leverage based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy. If you are a beginner, it is strongly recommended to start with extremely low leverage (such as 10:1 or 5:1). Your goal should be to survive and learn, not to get rich overnight.
2. Mistake Two: Ignoring the Margin Level.
Scenario: Focusing solely on profits and losses without noticing that the account's margin level is continuously declining.
Solution: Understand that the Margin Level = (Account Equity / Used Margin) × 100%. When this percentage falls below the broker's specified level (e.g., 100%), you will receive a margin call requiring you to deposit funds; if it continues to decline (e.g., below 50%), the broker will begin to force liquidation of your losing positions, regardless of how optimistic you are about the market outlook.
3. Mistake Three: Not considering overnight interest rates (Swap Rate).
Scenario: Holding high-leverage positions overnight, with overnight interest costs eroding account funds and potentially causing significant losses.
Solution: Before holding positions overnight, understand whether the overnight interest rates for different currency pairs are positive or negative. You can use our 【Swap Calculator】 to precisely calculate the cost of holding positions overnight.
4. Mistake Four: Lacking stop-loss discipline.
Symptom: Holding onto a position without setting a stop-loss order, hoping the market will reverse.
Solution: Always, always, always set stop-loss orders! This is the first rule to avoid margin calls. Stop-loss orders are the insurance you buy for this trade. Use our 【Stop Loss Calculator】 and 【Risk/Reward Calculator】 to scientifically set stop-loss levels, ensuring that any loss from a trade remains within your acceptable range (e.g., no more than 1%-2% of account funds).
Ⅵ. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What leverage ratio is suitable for beginners?
A: There is no one-size-fits-all answer, but an extremely conservative and safe recommendation is: do not exceed 10:1. Many professional traders use leverage ratios even lower than 5:1. Your goal is to control risk, not amplify gains. Start with low leverage and consider gradually adjusting it in small increments only after you can consistently profit for over six months.
Q2: What happens if my margin level drops too low?
A: You will go through the following process:
Warning: When your margin level falls below a specific value required by the broker (e.g., 100%), you will receive a Margin Call email or notification, alerting you that your account is underfunded and requiring you to deposit more funds or close some positions.
Forced liquidation: If you do not take action and the market continues to move against you, causing the margin level to further decline to another threshold (e.g., 50%), the broker's risk control system will automatically initiate forced liquidation (Stop-Out), starting with the positions with the largest losses until the margin level is restored to a safe level.
Q3: What are the differences in margin requirements among different brokers?
A: Yes, the differences can be significant. Key factors include:
Regulatory requirements: Regulatory bodies in different countries impose varying restrictions on maximum leverage (e.g., the EU's ESMA and the UK's FCA limit leverage on major currency pairs to 30:1 [[2]], while other regions may allow 500:1 or higher).
Currency pair type: Margin requirements typically vary between major currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD), minor currency pairs (e.g., EUR/GBP), and exotic currency pairs (e.g., USD/TRY), with exotic pairs generally requiring higher margins.
The broker's own risk management policies.
Therefore, our calculator provides a very precise estimate, but ultimately, you should rely on the real-time data on your broker's trading platform.
Q4: Is there a calculator for cryptocurrency leverage?
A: Cryptocurrency leverage trading operates similarly to forex, but it is highly volatile and carries greater risks. Our forex margin calculator is generally applicable to the most traded cryptocurrency/USD pairs (e.g., BTC/USD, ETH/USD). However, please note that the volatility of cryptocurrencies means your margin requirements may change rapidly, and the risk of margin calls is significantly higher than in forex.
Ⅶ. Mastering your risk management with our calculator suite
Now you understand that a skilled trader does not rely on a single calculator. Successful risk management is a systematic process.
After using this margin calculator, we strongly recommend that you immediately utilize other professional tools on our website to complete your pre-trade checklist:
1. Position Size Calculator: This is the most critical step! Based on your account balance, risk tolerance percentage, and stop-loss distance, determine the appropriate number of lots to trade. This ensures that even if the stop-loss is triggered, your losses remain within the planned and acceptable range.
2. Stop Loss Calculator & Risk/Reward Calculator: Based on your entry point and market analysis, set reasonable stop-loss and take-profit levels to ensure that the potential return on each trade exceeds the risk (e.g., a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:1.5).
3. Swap Calculator: If you plan to hold positions overnight (or even for several days), use this to calculate costs or gains and avoid “hidden” fees eroding your profits.
By combining these tools, you can build a robust risk management framework—the only reliable path to long-term survival and growth in the market.
Ⅷ. Conclusion: Trade smarter, not harder
Leverage is the most powerful gift the financial world has given to ordinary traders, but it is also the most dangerous trap. Respect it, and you will gain greater power; disregard it, and it will destroy you completely.
We hope this article and our free tools can become a reliable companion on your trading journey. Add it to your bookmarks, and take a minute to calculate and assess risks before clicking the "Buy" or "Sell" button each time. This simple habit, over time, will save you an immeasurable amount of money.
Start now: Use the calculator at the top of the page to input your next trade's parameters and see the results. Then, click on the links to our recommended tools to give your planned trade a comprehensive "check-up."
Risk Warning: Forex and margin derivatives trading involve high risk and are not suitable for all investors. You may lose part or all of your investment funds. Therefore, you should not invest funds you cannot afford to lose. The content and information provided on this website are for educational purposes only and do not constitute investment advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Before deciding to trade any financial product, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, trading experience, and risk tolerance. We recommend consulting an independent financial advisor to ensure you understand the risks involved.
Ⅸ. References and Links:
[1] Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) - "Product Intervention for Contract for Difference (CFD) and CFD-like options" (2018). This report details the high-risk nature of CFD (Contract for Difference, a common form of forex trading) products for retail clients and cites the proportion of clients who incur losses.
[2] European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) - "Questions and Answers on ESMA’s CFDs and binary options measures" (2023). This Q&A document explains why and how ESMA imposes restrictions on retail clients trading CFD products, including leverage limits.
[3] Babypips.com - "School of Pipsology". The world's most popular and authoritative free forex trading learning platform, whose teachings on leverage and margin are industry-standard references.

Leave a Comment: